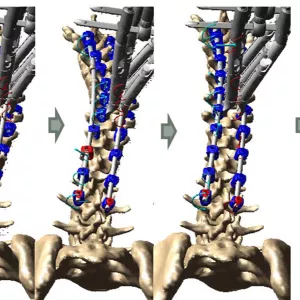
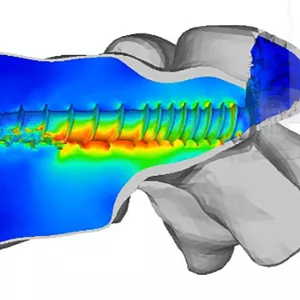
Carl Eric Aubin
Dr Aubin est professeur titulaire à l’École Polytechnique, chercheur au CHU Ste-Justine et professeur associé au département de chirurgie (Univ. Montréal). Il est double titulaire de la Chaire de recherche industrielle CRNSG/Medtronic en biomécanique de la colonne vertébrale et de la Chaire de recherche du Canada en génie orthopédique. Il est chef de l'Axe Maladies musculosquelettiques et réadaptation du CHU Ste-Justine, co-directeur du Groupe de recherche en sciences et technologies biomédicales et directeur du programme de formation MÉDITIS en technologies biomédicales.
Ses recherches couvrent l'étude et la modélisation biomécanique de la colonne vertébrale (scoliose), ainsi que l'évaluation, la conception et l'optimisation de traitements orthopédiques.
Il a publié plus de 150 articles scientifiques et 500 actes de conférences. Il a reçu plusieurs prix dont le prix jeune chercheur de la Fondation des Étoiles (2010). Il a formé plus de 100 étudiants (maîtrise, doctorat, postdoctorat).
Mes liens avec l'Acfas
ResponsableMes intérêts de recherche
Génie biomédical Biomécanique Scoliose Modélisation biomécanique Conception d'orthèses et implantsFormation
- 1991, Polytechnique Montréal, B. ing. (génie mécanique)
- 1995, Polytechnique Montréal, Ph.D. (génie mécanique), Biomécanique des corsets pour le traitement de la scoliose
- 1996, University of Vermont, Stage postdoctoral, Simulation de chirurgies de la scoliose
Mes contributions « Science et société »
Plus de 150 articles dans des revues scientifiques
Plus de 500 communications scientifiques lors de congrès
Entrevues:
Une pilule, une petite granule, Télé-Québec (Émission du 10/01/2013 sur la scoliose)
L'heure de Pointe, Radio Canada (Émission du 19/09/2023 sur le traitement de la scoliose)
Activités de formation:
café scientifique sur la scoliose,
symposium international sur les déformations 3D de la scoliose,
organisation de plusieurs colloques (Transfert de connaissances et transfert de technologies, Vers une carrière de chercheur-entrepreneur, Vers une carrière innovante, ouverte sur le monde, L’apport incontournable des modèles animaux en recherche innovatrice sur les maladies musculosquelettiques, ...)
Mes publications
148. Navéaux FL, Aubin CÉ, Larson AN, Polly DW Jr, Baghdadi YM, Labelle H,Implant distribution in surgically instrumented Lenke 1 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Does it affect curve correction?,Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2015 Jan 20. [Epub ahead of print]
147. Clin J, Aubin CE, Parent S, Biomechanical simulation and analysis of scoliosis correction using a fusionless intravertebral epiphyseal device,Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2015 Jan 12. [Epub ahead of print]
146. Auvinet E, Multon F, Aubin CE, Meunier J, Raison M, Detection of gait cycles in treadmill walking using a Kinect, Gait and Posture, 2014 Aug 20. [Epub ahead of print]
145. Aubin CE,Cammarata M, Wang X, Mac-Thiong J-M. Instrumentation strategies to reduce the risk of proximal junctional kyphosis in adult scoliosis: a detailed biomechanical analysis.Spine Deformity (Accepté, septembre 2014; sous presse)
143. Bianco R-J, Arnoux P-J, Wagnac E, Mac-Thiong J-M, Aubin CE. Minimizing pedicle screw pullout risks: a detailed biomechanical analysis of screw design and placement. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014 Jul 29. [Epub ahead of print]
142. Caouette C, Rauch F, Villemure I, Arnoux PJ, Gdalevitch M, Veilleux LN, Heng JL, Aubin CE. Biomechanical analysis of fracture risk associated with tibia deformity in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: a finite element analysis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2014 Jun;14(2):205-212.
141. Larson AN, Polly DW, Diamond B, Ledonio C, Richards BS 3rd, Emans JB, Sucato DJ, Johnston CE & Minimize Implants Maximise Outcomes Study Groups (incl. Aubin CE). Does higher anchor density result in increased curve correction and improved clinical outcomes in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis? Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2014 Apr 1;39(7):571-8.
140. Desrochers-Perrault F, Aubin CE, Wang X, and Schwend R.M. Biomechanical Analysis of Iliac Screw Fixation in Spinal Deformity Instrumentation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2014 Jun;29(6):614-21
139. Cobetto N, Parent S, Le May S, Clin J, Labelle H, Desbiens-Blais F, Aubin CE, Moreau A. Brace optimized with computer-assisted design and simulations are lighter, confortable and more efficient than plaster-casted braces for the treatment of Adolescent Idiopathic scoliosis. Spine Deformity 2014 Jul;2(4):276-284.
138. Wang X, Aubin CE, Rawlinson J, Coleman J. Correction capability in the 3 anatomical planes of different pedicle screw designs in scoliosis instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech 2014 May 26. [Epub ahead of print]
137. Cammarata M, Aubin CE, Wang X, Mac-Thiong JM. Biomechanical risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis: a detailed numerical analysis of surgical instrumentation variables, Spine 2014 Apr 15;39(8):E500-7.
136. Wang X, Aubin CÉ, J. Rawlinson, J. Coleman. Correction capability in the 3 anatomical planes of different pedicle screw designs in scoliosis instrumentation. J Spinal Dis Tech 2014 May 26 [Epub ahead of print].
135. Pasha S, Aubin CE, Parent S, Labelle H, Mac-Thiong J-M. Biomechanical Loading of the Sacrum in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2014 Mar; 29(3): 296-303
134. Pasha S,Aubin CE, Sangole A, Labelle H, Parent S, Mac-Thiong J-M. Three dimensional spino-pelvic relative alignment in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014 Apr 1;39(7):564-70.
133. Fradet L, Wagnac E, Aubin CE, Arnoux PJ. Biomechanics of thoracolumbar junction vertebral fractures from various kinematic conditions. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2014 Jan;52(1):87-94.
132. Bianco RJ, Arnoux PJ, Mac-Thiong JM, Wagnac E, Aubin CE. Biomechanical analysis of pedicle screw pullout strength.Comp Meth Biomech Biomed Eng. 2013 Jul;16 S.1:246-8.
131. Larson AN, Aubin CE, Polly DW, Ledonio C, Lonner BS, Shah SA, Sucato DJ, Lenke LG, Richards BS, Erickson MA, Emans JB, Weinstein SL & Minimize Implants Maximise Outcomes Study Groups. Are more screws better? A systematic review of anchor density and curve correction in AIS. Spine Deformity 2013 Jul; 1(4):237-247.
130. Foley G, Aubin CE, Parent S, Labelle H, d’Astous J, Johnston C, Sanders J. Physical Significance of the Rib Vertebra Angle Difference and its 3D Counterpart in Early Onset Scoliosis. Spine Deformity 2013 Jul; 1(4):259-265.
129. Lalonde NM, Petit Y, Aubin CE, Wagnac É, Arnoux P-J. Method to geometrically personalize a detailed finite model of the spine. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2013 Jul; 60(7):2014-2021.
128. Gervais J, Périé-Curnier D, Aubin CE. Sensitivity of MRI signal distribution within the intervertebral disc to image segmentation and data normalization. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng. 2014;17(12):1383-90. [Epub ahead of print]
127. M. Denninger, N. Huppé, M. Gou, C.E. Aubin & D. Rancourt, A tunable hand biofidelity-enhancing device for Hybrid III dummies, International Journal of Crashworthiness, 17:4, August 2012, pages 377-383
126. Cartiaux O, Banse X, Paul L, Francq BG, Aubin CE, Docquier PL. Computer-assisted planning and navigation improves cutting accuracy during simulated bone tumor surgery of the pelvis. Comput Aided Surg. 2013;18(1-2):19-26.
125. Driscoll M, Aubin CE, Moreau A, Wakula Y, Amini S, Parent S. Novel hemi-staple for the fusionless correction of pediatric scoliosis: influence on intervertebral discs and growth plates in a porcine model. J Spinal Dis Techn. 2013 Nov 07. [Epub ahead of print]
124. Desbiens-Blais F, Clin J, Parent S, Labelle H, Aubin CÉ. New Brace Design Combining CAD/CAM and Biomechanical Simulation for the Treatment of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012 Dec;27(10):999-1005.
123. Gervais J, Périé D, Parent S, Labelle H, Aubin CE. MRI signal distribution within the intervertebral disc as a biomarker of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and spondylolisthesis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012 Dec 3;13(1):239. [Epub ahead of print]
122. Wang X, Aubin CE, Labelle H, Parent S, Crandall D. Biomechanical analysis of corrective forces in spinal instrumentation for scoliosis treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Nov 15;37(24):E1479-87.
121. Martino J, Aubin CE, Labelle H, Wang X, Parent S. Biomechanical Analysis of Vertebral Derotation Techniques for the Surgical Correction of Thoracic Scoliosis: A Numerical Study Through Case Simulations and a Sensitivity Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013 Jan 15;38(2):E73-83.
120. Majdouline Y, Aubin CE, Wang X, Sangole A, Labelle H. Preoperative assessment and evaluation of instrumentation strategies for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: computer simulation and optimization. Scoliosis. 2012 Nov 26;7(1):21
119. Wang X, Aubin CÉ, Labelle H, Parent S, Crandall D. Biomechanical analysis of corrective forces in spinal instrumentation for scoliosis treatment.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Nov 15;37(24):E1479-87.
118. Wagnac É, Arnoux PJ, Garo A, Aubin CÉ. Finite element analysis of the influence of loading rate on a model of the full lumbar spine under dynamic loading conditions. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2012 Sep; 50(9):903-15.
117. Beaudette K, Strupler M, Benboujja F, Parent S, Aubin CÉ, Boudoux C. Optical coherence tomography for the identification of musculoskeletal structures of the spine. Biomedical Optics Express 2012 Mar 1; 3(3):533-42.
116. Sevrain A, Aubin CÉ, Gharbi H, Wang X, Labelle H. Biomechanical evaluation of predictive parameters of progression in adolescent isthmic spondylolisthesis. Scoliosis. 2012 Jan 18; 7(1):2.
115. Wang X, Aubin CÉ, Crandall D, Parent S, Labelle H. Biomechanical analysis of four types of pedicle screws for scoliotic spine instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Jun 15;37(14):E823-35.
114. Wagnac E, Garo A, Arnoux PJ, El-Rich M, Aubin CE. Calibration of hyperelastic material properties of the human lumbar intervertebral disc under fast dynamic compressive loads.J.Biomech Eng. 2011 Oct; 133(10):101007.
113. Wang X, Aubin CÉ,Robitaille I, Labelle H. Biomechanical comparison of alternative densities of pedicle screws for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,Eur Spine J. 2012 Jun;21(6):1082-90.
112. Garo A, Arnoux PJ, Wagnac E, Aubin CE. Calibration of the mechanical properties in a finite element model of a lumbar vertebra under dynamic compression up to failure. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2011 Dec;49(12):1371-9.
111. Driscoll M, Aubin CE, Moreau A, Wakula Y, Sarwark JF, Parent S. Spinal growth modulation using a novel intravertebral epiphyseal device in an immature porcine model. Eur Spine J. 2012 Jan; 21(1):138-44.
110. Driscoll M, Aubin CE, Parent S, Moreau A. Biomechanical comparison of fusionless growth modulation corrective techniques in pediatric scoliosis.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2011 Dec; 49(12):1437-45.
109. Clin J, Aubin CÉ,Lalonde NM, Parent S, Labelle H. A new method to include the gravitational forces in a finite element model of the scoliotic spine.Med Biol Eng Comp2011 Aug; 49(8):967-77.
108. Shi L, Wang D, Driscoll M, Villemure I, Chu W, CY Cheng J, Aubin CÉ. Biomechanical analysis and modeling of different vertebral growth patterns in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and healthy subjects.Scoliosis 2011 May23; 6(1):11
107. Driscoll C, Aubin CE, Labelle H, Dansereau J, Assessment of two novel surgical positions for the reduction of scoliotic deformities: lateral leg displacement and hip torsion,Eur Spine J 2011 Oct;20(10):1711-9.
106. Driscoll C, Aubin CE,Canet F, Labelle H, Horton W, Dansereau J. Biomechanical study of patient positioning during surgery of the spine: influence of lower limb positioning on spinal geometry,J Spinal Disord Tech 2012 Apr;25(2):69-76.
105. Wang X, Aubin CÉ, Crandall D, Labelle H. Biomechanical modeling and analysis of the direct incremental segmental translation system for the instrumentation of scoliotic deformities,Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011 Jul; 26(6):548-55.
104. Driscoll C, Aubin CE, Canet F, Labelle H. Impact of prone surgical positioning on the scoliotic spine.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011 Mar 16. [Epub ahead of print]
103. Phan P, Mezghani N, Aubin CÉ, de Guise J, Labelle H. Computer algorithms and applications used to assist the evaluation and treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A review of published articles 2000-2009.Eur. Spine J. 2011 Jul;20(7):1058-68.
102. Aubin CÉ, Bellefleur C, Joncas J,de Lanauze D, Kadoury S, Blanke K, Parent S, Labelle H. Reability and accuracy analysis of a new semi-automatic radiographic measurement software in adult scoliosis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011 May 20;36(12):E780-90
101. Clin J, Aubin CÉ, Parent S, Labelle H. Biomechanical modeling of brace treatment of scoliosis: effects of gravitational loads.Med Biol Eng Comp 2011 Jul;49(7):743-53.
100. Labelle H, Aubin CÉ, Lenke L, Newton P, Stokes I, Jackson R, Parent S. Seeing the spine in 3D: how will it change what we do?,J Pediatr Orthop. 2011 Jan-Feb;31(1 Suppl):S37-45.
99. Wang X, Aubin CÉ, Crandall D, Labelle H. Biomechanical comparison of force levels in spinal instrumentation using monoaxial versus multi degree of freedom post-loading pedicle screws.Spine 2011 Jan 15;36(2):E95-E104.
98. Chagnon A, Aubin CÉ, Villemure I. Biomechanical influence of disk properties on the load transfer of healthy and degenerated disks using a poroelastic finite element model.J Biomech Eng 2010 Nov; Vol. 132: 111006/1-8.
97. Clin J, Aubin CÉ, Parent S, Labelle H. A Biomechanical Study of the Charleston Brace for the Treatment of Scoliosis,Spine, (Phila Pa 1976). 2010 Sep 1;35(19):E940-7.
96. Fayant P, Girlanda O, Chebli Y, Aubin CÉ, Villemure I, Geitmann A. Finite Element Model of Polar Growth in Pollen Tubes. Plant Cell. 2010 Aug;22(8):2579-93.
95. Lalonde NM, Villemure I, Pannetier R, Parent S, Aubin CÉ. Biomechanical modeling of the lateral decubitus posture during corrective scoliosis surgery.Clin Biomech Jul;25(6):510-6.
94. Driscoll C, Aubin CÉ,Canet F, Dansereau J, Labelle H. The impact of intra-operative sternum vertical displacement on the sagittal curves of the spine,Eur Spine J, 2010 Mar; 19(3):421-6.
93. Sangole A, Aubin CÉ, Labelle H, Lenke L, Jackson R, Newton P, Stokes IA; The Central Hip Vertical Axis: A Reference Axis for the Scoliosis Research Society Three-Dimensional Classification of Idiopathic Scoliosis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010 May 20;35(12):E530-4.
92. Clin J, Aubin CÉ, Parent S, Sangole A, Labelle H. Comparison of the biomechanical 3D efficiency of different brace designs for the treatment of scoliosis using a finite element model,European Spine Journal, 2010 Jul;19(7):1169-78.
91. Phan P, Nezghani N, Nault ML, Aubin CÉ, Parent S, de Guise J, Labelle H. A decision tree can increase accuracy when assessing curve types according to Lenke classification of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010 May 1;35(10):1054-9.
90. Sangole AP, Aubin CE, Labelle H, Stokes IA, Lenke LG, Jackson R, Newton P. Letter to the Editor,Spine. 2010 Feb 15;35(4):465-6.
89. Pasha S, Sangole A, Aubin CÉ, Parent S, Mac-Thiong JM, Labelle H. Characterizing pelvis dynamics in adolescent with idiopathic scoliosis,Spine 2010 Aug 1;35(17):E820-6.
88. Clin J, Aubin CÉ, Sangole A, Labelle H, Parent S. Correlation between immediate in-brace correction and biomedical effectiveness of brace treatment in Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,Spine 2010 Aug 15;35(18):1706-13.
87. Chevrefils C, Cheriet F, Aubin CÉ, Grimard G. Statistical and Spectral Texture Analysis for Automatic Segmentation of Intervertebral Disks of Scoliotic Spines from MR Images,IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2009 Jul;13(4):608-20.
86. Bagnall KM, Grivas TB, Alos N, Asher M, Aubin CÉ, Burwell RG, Dangerfield PH, Edouard T, Hill D, Lou E, Moreau A, O'Brien J, Stokes I, Weiss HR, Raso J. The International Research Society of Spinal Deformities and its contribution to science.Scoliosis 2009 Dec 22; 4(1):28.
85. Driscoll M, Aubin CE, Moreau A, Villemure I, Parent S., The role of spinal concave-convex biases in the progression of idiopathic scoliosis.Europ Spine J, 2009 Feb; 18(2):180-7.
84. Duke K, Aubin CÉ, Dansereau J, Koller A, Labelle H. Dynamic positioning of scoliotic patients during spine instrumentation surgery, J Spinal Disord Tech, 2009 May;22(3):190-6.
83. El-Rich M, Arnoux PJ, Wagnac E, Brunet C, Aubin CÉ. Finite Element Investigation of the Loading Rate Effect on the Spinal Load-Sharing Changes under Impact Conditions,J Biomech, 2009 Jun 19; 42(9):1252-62.
82. El-Rich M, Villemure I, Labelle H, Aubin CÉ. Mechanical loading effects on isthmic spondylolytic lumbar segment: Finite element modelling using a personalised geometry.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin, 2009; 12(1): 13-23.
81. Hayashi K, Upasani VV, Pawelek JB, Aubin CÉ, Labelle H, Lenke LG, Jackson R, Newton PO. Three-Dimensional Analysis of Thoracic Apical Sagittal Alignment in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis,Spine (2009) 34(8):792–797
80. Lamarre ME, Parent S, Labelle H, Aubin CÉ, Joncas J,Cabral A, Petit Y. Assessment of spinal flexibility in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Suspension versus side-bending radiography.Spine 2009; 34(6): 591-7.
79. Lin H, Aubin CÉ, Parent S, Villemure I, Mechanobiological bone growth: comparative analysis of two biomechanical modeling approaches,Med Biol Eng Comp 2009 Apr;47(4):357-66.
78. Majdouline Y, Aubin CÉ, Sangole A, Labelle H. Computer simulation for the optimization of instrumentation strategies in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009 Nov; 47(11):1143-54. Epub 2009 Aug 11.
77. Nault ML, Labelle H, Aubin CÉ, Balazinski M. Fuzzy logic assisted surgical planning in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,J Spinal Disorders & Techniques, 2009; 22(4):263-9
76. Robitaille M, Aubin CÉ, Labelle H. Effects of alternative instrumentation strategies in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A biomechanical analysis.J Orthop Res, 2009; 27(1): 104-13.
75. Sangole AP, Aubin CÉ, Labelle H, Stokes IA, Lenke LG, Jackson R, Newton P. Three-dimensional classification of thoracic scoliotic curves.Spine, 2009 Jan; 1;34(1): 91-9.
74. Stokes IA, Sangole AP, Aubin CÉ. Classification of scoliosis deformity three-dimensional spinal shape by cluster analysis.Spine, 2009 Mar; 15; 34(6): 584-90.
73. Aubin CÉ, Labelle H, Chevrefils C,Desroches G,Clin J, Boivin A. Pre-operative planning simulator for spinal deformity surgeries,Spine 2008;33(20):2143–2152.
72. Duke K, Aubin CÉ, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Computer simulation for the optimization of patient positioning in spinal deformity instrumentation surgery.Med Biol Eng Comput 2008;46(1):33-41.
71. Schmid E, Aubin CÉ, Moreau A., Sarwark J, Parent S. A novel fusionless vertebral physeal device inducing spinal growth modulation for the correction of spinal deformities,Europ Spine J. 2008 Oct; 17(10):1329-35.
70. Zoabli G, Mathieu PA, Aubin CE, Magnetic resonance imaging of the erector spinae muscles in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: implication for scoliotic deformities.Scoliosis. 2008 29; 3:21.
69. Aubin CÉ, Labelle H, Cheriet F, Villemure I, Mathieu PA, Dansereau J. Tridimensional evaluation and optimization of the orthotic treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Médecine Science (Paris), 2007 Nov; 23(11):904-9.
68. Aubin CÉ, Labelle H,Ciolofan O. Variability of spinal instrumentation configurations in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.European Spine J; Jan. 2007; 16(1):57-64.
67. Clin J, Aubin CÉ, Labelle H. Virtual prototyping of a brace design for the correction of scoliotic deformities,Med Biol Eng Comput, May 2007; 45(5):467-73 EPU Mars 17.
66. Cloutier L, Aubin CÉ, Grimard G. Biomechanical study of anterior spinal instrumentation configurations;European Spine J, Jul 2007;16(7):1039-45
65. Desroches G, Aubin CÉ, Sucato DJ, Rivard CH. Simulation of an anterior spine instrumentation in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis using a flexible multi-body model.Med Biol Eng Comput, 2007; 45(8) :759-68
64. Huynh AM, Aubin CÉ, Mathieu PA, Labelle H. “Simulation of progressive spinal deformities in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy using a biomechanical model integrating muscles & vertebral growth modulation”,Clin Biomech, May 2007; 22(4): 392-9
63. Huynh AM, Aubin CÉ, Rajwani T, Bagnall K, Villemure I. Pedicle growth asymmetry as a cause of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a biomechanical study;European Spine J, April 2007 16(4):523-9.
62. Labelle H, Bellefleur C, Joncas J, Aubin CÉ, Cheriet F. Preliminary evaluation of a computer assisted tool for the design and adjustment of braces in idiopathic scoliosis : a prospective and randomized study,Spine, April 2007; 32(8):835-43
61. Lafortune P, Aubin CÉ,Boulanger H, Villemure I, Bagnall KM, Moreau A. Biomechanical simulations of the scoliotic deformation process in the pinealectomized chicken: a feasibility study.Scoliosis, 2007 Nov 9; 2:16.
60. Majdouline Y, Aubin CÉ, Robitaille M, Sarwark J, Labelle H. Scoliosis correction objectives in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,J Pediatr Orthop, Oct 2007; 27(7):755-781
59. Nault ML, Labelle H., Aubin CÉ, Balazinsky M., The use of fuzzy logic to select which curves need to be instrumented and fused in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a feasibility study.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007 Dec; 20(8):594-603.
58. Robitaille M, Aubin CÉ, Labelle H. Intra and interobserver variability of preoperative planning for surgical instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Eur Spine J, Oct 2007; 16(10):1604-14.
57. Sarwark J, Aubin CÉ, Growth considerations of the immature spine,J Bone Jt Surg; Feb. 2007; 89:8-13.
56. Sylvestre PL, Villemure I, Aubin CÉ. Finite element modeling of the growth plate in a detailed spine model,Med Biol Eng Comput, Oct 2007; 45(10):977-88. Epub 2007 Aug 9.
55. Zoabli G, Mathieu PA, Aubin CÉ. Back muscles biometry in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,Spine J. 2007 May - June; 7(3):338-344.
54. Bolduc JF, Lewis LJ, Aubin CÉ, Geitmann A. Finite element analysis of geometrical factors in the micro-indentation experiment performed on pollen tubes.Biomech & Model in Mechanobiol; Nov. 2006;5(4): 227-36
53. Koutchouk M, Aubin CÉ, Gou M. Computer modeling of lift trucks and operators to simulate lateral tipover.International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2006; 11(5); 485-493
52. Carrier J, Aubin CE, Trochu F, Labelle H. Optimisation of rib surgery parameters for the correction of scoliotic deformities using dual kriging,J Biomech Eng. Aug. 2005;127:4, 680-691
51. Duke K, Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Biomechanical simulations of scoliotic spine correction due to prone position and anaesthesia prior to surgical instrumentation.Clin Biomech 2005, 20(9):923–31
50. Aubin CE, Goussev V,Petit Y. Biomechanical modeling of segmental instrumentation for surgical correction of 3D spinal deformities using Euler-Bernoulli thin-beam elastic deformation equations,Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing. 2004; 42:216-21.
49. Carrier J, Aubin CE, Villmeure I., Labelle H. Biomechanical modeling of growth modulation following rib shortening or lengthening in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,Med Biol Eng Comput, 2004, 42:4, 541-548
48. Mac-Thiong J-M, Labelle H, Aubin CE. Thoracic pedicle screw insertion using a transpedicular drill guide. A preliminary study.J Spinal Disorders & Techniques. 2004; 19(7):29-32
47. Mac-Thiong J-M, Petit Y, Aubin CE, Delorme S, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Biomechanical evaluation of the Boston brace for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Relationship between strap tension and brace forces.Spine. 2004; 29:1, 26-32.
46. Périé D, Aubin CE, Petit Y, Labelle H, Dansereau J. personalized biomechanical simulations of orthotic treatment in idiopathic scoliosis,Clinical Biomechanics. 2004; 19(2): 190-5.
45. Périé D, Aubin CE, Lacroix M, Lafon Y, Labelle H. Biomechanical modelling of orthotic treatment of the scoliotic spine including a detailed representation of the brace-torso interface.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2004; 42:339-44.
44. Petit Y, Aubin CE, Labelle H. Spinal shape changes resulting from scoliotic spine instrumentation expressed as intervertebral rotations and centres of rotation.J Biomechanics. 2004; 37(2): 173-180.
43. Petit Y, Aubin CE, Labelle H. Patient-specific mechanical properties of a flexible multi-body model of the scoliotic spine.Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2004; 42(1):55-60.
42. Villemure I,Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Biomechanical simulations for the spine deformation process in AIS from different pathogenesis hypotheses.Eur Spine J. 2004; 13(1):83-90
41. Aubin CE,Petit Y, Stokes IAF,Poulin F, Gardner-Morse M, Labelle H. Biomechanical modeling of posterior instrumentation of the scoliotic spine.Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering 6[1], 27-32. 2003.
40. Delorme S, Petit Y, de Guise JA, Aubin CE, Dansereau J. Assessment of the 3-D reconstruction and High-Resolution Geometrical Modeling of the Human Skeletal Trunk From 2-D Radiographic Images.IEEE Trans. on Biomedical Engineering. 2003; 50(8):989-998.
39. Mac-Thiong JM, Labelle H, Rooze M, Feipel V, Aubin CE. Evaluation of a transpedicular drill guide for pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine.Europ Spine. 12:542-547. 2003.
38. Odermatt D, Mathieu PA, Beauséjour M, Labelle H, Aubin CE. Electromyography of scoliotic patients treated with a brace.J Orthop Res, 2003; 21(5) :931-936.
37. Périé D, Aubin CE,Petit Y, Beauséjour M, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Boston brace correction in idiopathic scoliosis : a biomechanical study.Spine. 2003(15) :1672-1677
36. Salako F, Aubin CE, Fortin C, Labelle H. Développement de guides chirurgicaux personnalisés, par prototypage rapide, pour l’installation de vis pédiculaires.Innov Technol Biol Med-RBM. 2003;24: 199-205.
35. Delorme S, Labelle H, Aubin CE. Is Cobb angle progression a good indicator in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis?Spine, 27[6], E145-151. 2002.
34. Feipel V, Aubin CE, Ciolofan O C, Beauséjour M, Labelle H, Mathieu PA. Electromyogram and kinematic analysis of lateral bending in idiopathic scoliosis patients.Med Biol Eng Comp [40], 497-505. 2002.
33. Gréalou L, Aubin CE, Labelle H. Rib cage surgery for the treatment of scoliosis: a biomechanical study of correction mechanisms.J Orthop Research 20[5], 1121-8. 2002.
32. Mac-Thiong JM, Labelle H, Duong L, Aubin CE. A new technique for intraoperative analysis of the trunk geometry in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Can J Surg 45 :3, 219-223. 2002.
31. Mac-Thiong J-M, Labelle H, Petit Y, Aubin CE. The effect of the Relton-Hall operative frame on trunk deformity in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Europ Spine J 11[6], 556-560. 2002.
30. Petit Y, Aubin CE, Labelle H. 3-D Imaging for the surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Canadian Journal of Surgery 45[6], 453-458. 2002.
29. Villemure I,Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Simulation of progressive deformities in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using a biomechanical model integrating vertebral growth modulation.Journal of Biomechanical Engineering [124], 784-790. 2002.
28. Villemure I,Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Modélisation biomécanique de la croissance et de la modulation de croissance vertébrale pour l’étude des déformations scoliotiques : étude de faisabilité.Innov Technol Biol Med 23[2], 109-117. 2002.
27. Pavec D, Aubin CE, Aissaoui R, Parent F, Dansereau J. Kinematic modeling for the assessment of wheelchair user’s stability.IEEE Trans Rehab Eng. 9[4], 362-368. 2002.
26. Villemure I,Aubin CE, Grimard G, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Progression of vertebral and spinal three-dimensional deformities in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis- a longitudinal study.Spine 26[20], 2244-2250. 2001.
25. Delorme S, Violas P, Dansereau J, de Guise JA, Aubin CE, Labelle H. Preoperative and postoperative three-dimensional changes of the rib cage after posterior instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.European Spine Journal 10, pp. 101-106. 2000.
24. Delorme S, Labelle H, Aubin CE, de Guise JA, Rivard CH, Poitras B et al. A Three-Dimensional Radiographic Comparison of Cotrel-Dubousset and Colorado Instrumentations for the Correction of Idiopathic Scoliosis.Spine 25[2], 205-210. 2000.
23. Delorme S, Labelle H, Aubin CE, De Guise JA, Rivard CH, Poitras B et al. Intra-operative Comparison of Two Instrumentation Techniques for the Correction of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis - Rod Rotation and Translation.Spine 25[6], 77S-83S. 2000.
22. Gignac D, Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Optimization Method for 3d Bracing Correction of Scoliosis Using a Finite Element Model.European Spine Journal 9[3], 185-190. 2000.
21. Mac-Thiong JM, Labelle H, Vandal S, Aubin CE. Intra-operative tracking of the trunk during surgical correction of scoliosis: a feasibility study.Computer Aided Surgery 5[5], 333-42. 2000.
20. Aubin CE, Labelle H, Ruszkowski A, Petit Y,Gignac D, Joncas J et al. Variability of strap tension in brace treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Point of view.Spine, 24[4], 349-354. 1999.
19. Beauséjour M, Aubin CE, Feldman AG, Labelle H. Simulations de tests d'inflexion latérale à l'aide d'un modèle musculo-squelettique du tronc.Ann. Chirurgie, 53[8], 742-750. 1999.
18. Cheriet F, Delorme S, Dansereau J, Aubin CE, de Guise JA, Labelle H. Perioperative radiographic reconstruction of the scoliotic vertebral column.Ann Chir, 53[8], 808-15. 1999.
17. Cheriet F, Dansereau J, Petit Y, Aubin CE, Labelle H, de Guise JA. Towards the Self-Calibration of a Multiview Radiographic Imaging System for the 3D Reconstruction of the Human Spine and Rib Cage.International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 13[5], 761-779. 1999.
16. Delorme S, Labelle H, Aubin CE, de Guise JA, Rivard CH, Poitras B et al. Intraoperative Comparison of Two Instrumentation Techniques for the Correction of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis - Rod Rotation and Translation.Spine, 24[19], 2011-2017. 1999.
15. Delorme S, Labelle H, Aubin CE, de Guise JA, Dansereau J. Comparison between clinical Cobb angles and measurements performed on vertebral bodies, pedicle centroids and spinous processes.Ann Chir, 53[8], 792-797. 1999.
14. Mac-Thiong JM, Aubin CE, Dansereau J, de Guise JA, Brodeur P, Labelle H. Registration and geometric modelling of the spine during scoliosis surgery: a comparison study of different pre-operative reconstruction techniques and intra-operative tracking systems.Medical and Biological Engineering Computing 37[4], 445-450. 1999.
13. Mathieu PA, Aubin CE. Activité musculaire du dos lors de flexions/extensions chez un second groupe de sujets normaux.Annales de chirurgie 53[8], 761-772. 1999.
12. Papin P, Labelle H, Delorme S, Aubin CE, de Guise J, Dansereau J. Long-Term Three-Dimensional Changes of the Spine After Posterior Spinal Instrumentation and Fusion in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. European Spine Journal 8 [1], 16-21. 1999.
11. Villemure I,Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Petit Y, Labelle H. Correlation study between spinal curvatures and vertebral and disk deformities in idiopathic scoliosis.Ann Chir 53[8], 798-807. 1999.
10. Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Petit Y, Parent F, de Guise JA, Labelle H. Three-dimensional measurement of wedged scoliotic vertebrae and intervertebral disks.European Spine Journal 7[1], 59-65. 1998.
9. Gignac D, Aubin CE, Dansereau J,Poulin F, Labelle H. Étude biomécanique de nouveaux concepts de traitement orthotique pour la correction de la scoliose.Annales de Chirurgie 1998; 52: pp. 795-800.
8. Poulin F, Aubin CE, Stokes IAF, Gardner-Morse M, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Modélisation biomécanique de l’instrumentation du rachis scoliotique à l’aide de mécanismes flexibles.Annales de Chirurgie 1998; 52: pp. 761-767.
7. Aubin CE, Dansereau J, de Guise JA, Labelle H. Rib cage-spine coupling patterns involved in brace treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Spine 22[6], 629-635. 1997-03.
6. Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Parent F, Labelle H, de Guise JA. Morphometric evaluations of personalized 3D reconstructions and geometric models of the human spine.Medical and biological engineering and computing 35[6], 611-618. 1997.
5. Poulin F, Aubin CE,Gignac D, Dansereau J, de Guise JA, Labelle H. Nouvelle approche orthotique de traitement 3D de la scoliose: étude biomécanique.Ann. chirurgie 51[8], 933. 1997.
4. Aubin CE, Dansereau J, de Guise JA, Labelle H. A study of biomechanical coupling between spine and rib cage in the treatment by orthosis of scoliosis.Annales de Chirurgie 50[8], pp. 641-650. 1996.
3. Aubin CE, Descrimes JL, Dansereau J, Skalli W, Lavaste F, Labelle H. Geometrical modeling of the spine and the thorax for the biomechanical analysis of scoliotic deformities using the finite element method.Ann Chir 49[8], 749-61. 1995.
2. Descrimes JL, Aubin CE, Skalli W. et al., Modelling of facet joints in a finite element model of the scoliotic spine and thorax: mechanical aspects.Rachis 7, (1995) pp 301-314.
1. Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Biomechanical simulation of the effect of the Boston brace on a model of the scoliotic spine and thorax.Ann Chir 47[9], 881-887. 1993.
Mes prix et distinctions
- 2015, Chaire de recherche du Canada (niveau 1) en génie orthopédique
- 2006-..., Chaire de recherche industrielle CRSNG-Medtronic en biomécanique de la colonne vertébrale
- 2011, Whitecloud Award, IMAST, Copenhague (en nomination, finaliste pour la meilleure communication)
- 2010, Prix de reconnaissance jeune chercheur, Fondation des étoiles
- 2004-2007, Professeur honoraire, Université Sichuan, Chine
- 2004, Prix Pierre Labelle - 34ème congrès, Société de Scoliose du Québec
- 2001-2010, Chaire de recherche du Canada (niveau 2) - innovations en génie orthopédique